Welcome to QUBO: From Zero to Hero (I’m not Hero yet 😄 ).
I recently joined a company working on quantum computing, optimization, and AI. While learning the tech stack, I kept seeing QUBO everywhere but it wasn’t always clear what it really meant or how people were using it day to day.
This series is my way of understanding what problems are being solved and what people around me are actually doing.
It is also how I reflect and organize my own understanding while learning QUBO.
I start from zero, keep things simple, and focus on practical understanding.
If you’re also new or curious, let’s learn together.
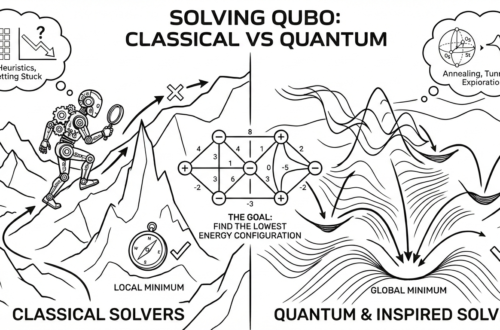
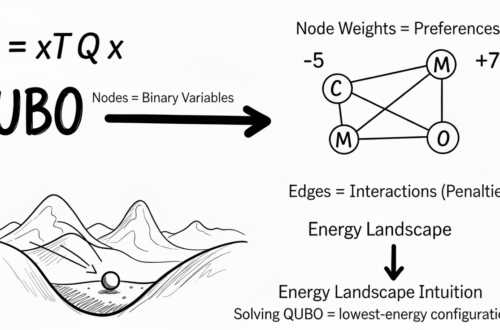
1. What is QUBO?
QUBO is a way of writing decision problems using:
- binary choices (0 or 1)
- a formula that adds penalties when rules are broken
- a solver that tries to make the formula as small as possible
Think of QUBO like a game:
- You try combinations of 0s and 1s
- Breaking rules adds penalty points
- The best answer is the one with lowest score
If the score becomes 0, that means “perfect — all rules satisfied.”
2. Why learn QUBO?
Because many real-life problems can be turned into QUBO and solved automatically. Here are typical examples QUBO handles well:
Choosing the Best Combination (Knapsack Problem)
You pick items to put in a backpack:
- maximize value
- but don’t exceed weight
- and follow some conditions
QUBO evaluates all choices.
Scheduling (Classes, Meetings, Shifts)
You want:
- no conflicts
- respect availabilities
- minimal gaps
- balanced load
All these constraints can be written in QUBO.
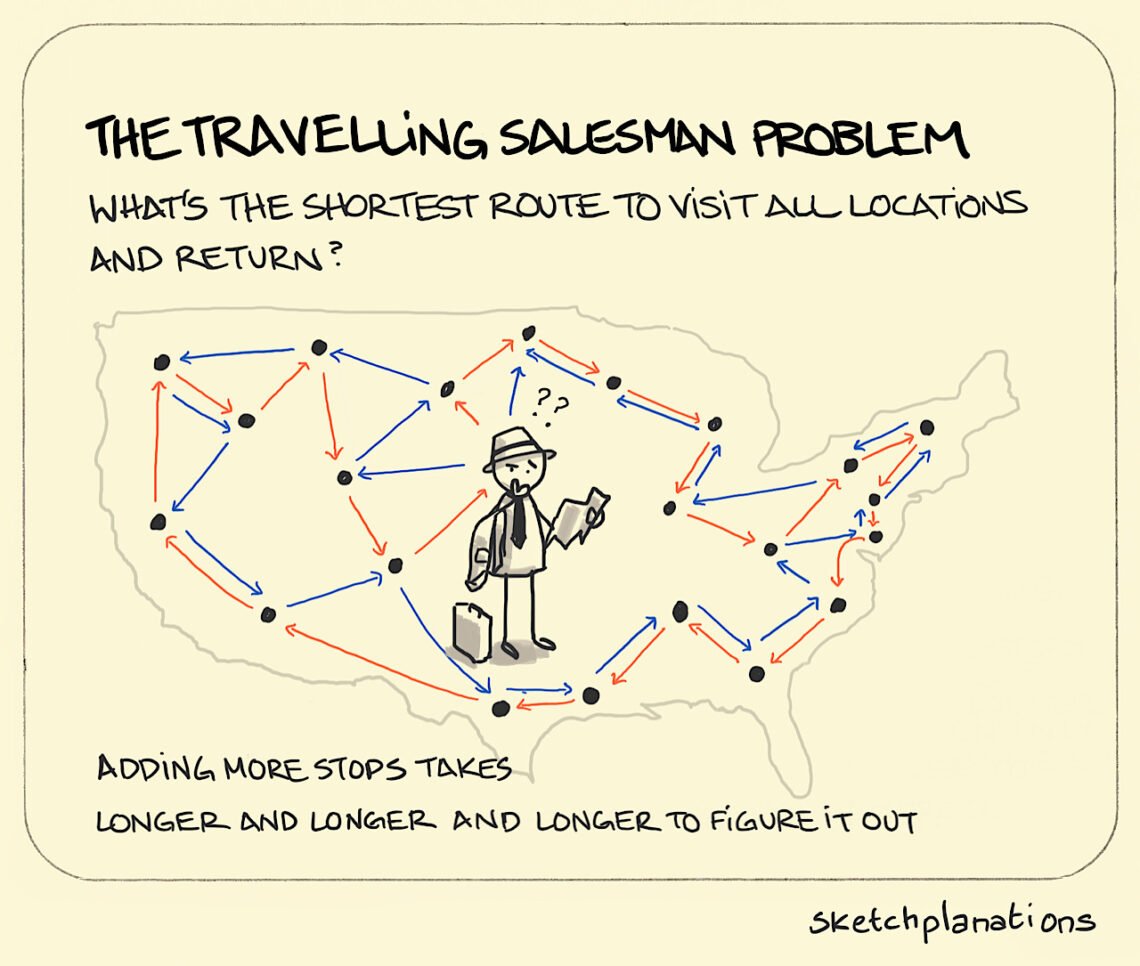
Route Optimization (Delivery, Travel)
Example: Deliver pizza to 10 houses in the shortest path
→ A very hard problem
→ QUBO can solve it

Task Assignment
Which person should do which task?
Match skills, avoid overload, respect preferences.
QUBO handles these “many choices + many rules” problems naturally.
3. Super simple example: Choose 1 drink
Let’s start very simple.
You have two drinks: Coke and Milk Tea
Variables:
- x = 1 if you choose Coke
- y = 1 if you choose Milk Tea
Rule: Choose exactly ONE drink.
We express this rule as: QUBO = (x + y − 1)²
This formula becomes:
- 0 when the rule is satisfied
- positive number when the rule is broken
4. Testing all drink choices
Check all combinations:

The solver will pick solutions with 0 penalty → choose exactly 1 drink.
5. Assessment: Try it yourself
Now try a slightly bigger case.
You now have 3 drinks:
- Coke
- Milk Tea
- Orange Juice
Variables:
- x = 1 if you choose Coke
- y = 1 if you choose Milk Tea
- z = 1 if you choose Orange Juice
Rule:
Choose exactly ONE.
Your task:
Write the QUBO formula for this rule.
(Hint: in the 2-drink case, we used (x + y − 1)².)